McQuinn: DDR and the Internal Organization of Non-State Armed Groups
Tags: papers
Summary
Argues that ddr can be seen through rebel groups with their command structure and financing
Posists two axes:
| Formal Command Structure | Informal Command Structure | |
|---|---|---|
| Community Based Resource | CPN-Maoists | Thubactis Battlaion |
| Resource Based Resource | FARC-EP | AUC |
Compares maoist fighters in nepal, FARC in Colombia, thubactics battlion, and autodefensas unidas de colombia (AUC)
Links to Kalyvas - The Logic of Violence in Civil War and
- Roy Licklider’s seminal study that that 5 years is a standard for peace
- Also talks about liberia’s war based networks and command structures playing a role in DDR
- Notes that relationships between group’s internal structure and DDR trajectories have not been studied
Previous research
- Civil wars did not account for heterogenity of non-state armed groups until quite late
- Several factors
- frequency and severity
- economic drivers
- onset
- duration
- outcomes
- peacemaking negotions
- Paper used
- recruitment strategies
- rebel governance
- economic models for group formation
- prevalance of child soldiers
- the strategies behind violence against communities
- fighting tactics
- pre-war social networks
- role of gender
- persistence of small and lightly armed guerilla groups
- Uses Weinstein: Resources and the Information Problem in Rebel Recruitment
- incorporates Staniland - Networks of Rebellion
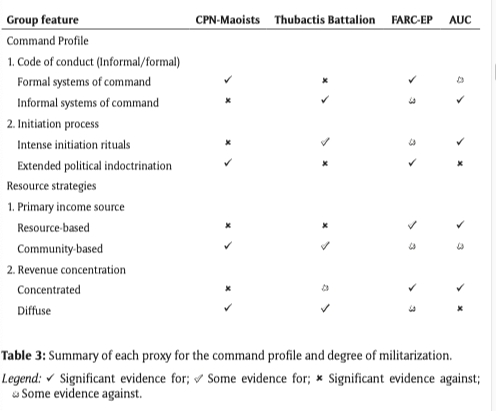
Command Profile and Economic Profile
- Comand profiles can be driven by terror or internal organization
- Quasi-judicial processes can enforce greater cohesion, leading to lower levels of uncertainty
- maoist fighters in nepal did this, were able to prevent from going back to war despite long term reintegration being stalled
- terror caused by individual groups can lead to higher levels of uncertainty, ruling through fear
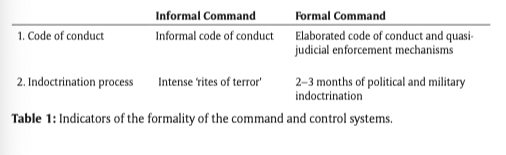
- Financing can be either predation on the local community, which leads to higher levels of organizatoin, or resource-extractive based, leading to lower levels of coordination